Proto History of Himachal Pradesh is closely linked with Proto History of South Asia. It is believed that Modern Humans evolved in East Africa and started migrating toward the Arabian Peninsula and finally entered South Asia around 75000-70000 years ago. Archeologists have found many Stone Tools from Lower Paleolithic age to Upper Paleolithic age from Shivalik hills of Pakistan, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh , Uttarakhand , Nepal etc.
First wave of migration ( 70000-60000 years Ago )
The first migrant followed the coastal Pass by crossing the Red Sea and reached the Andaman and finally into Australia. Haplogroup H is believed to have evolved in the Indian subcontinent approximately 30,000 to 40,000 years ago, who along with Haplogroup C and F represents the descendants of the original Migrants who left Africa and settled along the coast of the Indian Ocean. Unlike other haplogroup that arrived later (like R1a from Central Asia), H is truly “autochthonous” (native to the soil). Today we call them Ancient Ancestral of South India (AASI).
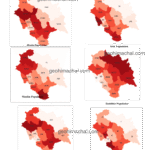
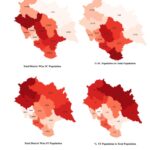
In Himachal Pradesh these people are spread right from Shivalik hills to deep interior valleys of Kinnaur and Lahaul Spiti. Thus they are the original inhabitants of Himachal Pradesh. Today Dom like people preserve the oldest genetic layer of the region and descend partly from the earliest modern humans who settled the Indian subcontinent, making them representatives of the deepest ancestral population of Himachal Pradesh.
Pre-farming Iranian Hunter-Gatherers ( 12000-10000 years ago )
Around 12000-10000 years Irani people came to India and mixed with early hunter gathers. These people came from the Fertile Crescent region of Middle East , these people are also called Zagros people named after the Zagros mountain range of Iran.
These migrants mixed with earlier Hunter Gathers and laid down the foundation of Indus Valley Civilization. They began the Neolithic Agricultural Revolution in South Asia indigenously. Rakhigarhi DNA has proved that agriculture in India started independently without the influence of Fertile Crescent, however few scholars believe that they might have taken input from fertile crescent.
In Himachal Pradesh we lack the publicly available data of Irani Farmers related Ancestry in population but it may be a significant part of ancestry, particularly of the Farming Community. With the presence of the Ropar Harappan site near Shivalik foothills , we can definitely conclude that these farmers must have migrated into the hills lately after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization. These people left a deep impact on South Asian culture. ( Read More about Indus Valley Culture).
Austro Asiatic People ( 2000 BCE and 1500 BCE )
Asutro-Asiatic people also known as Kol/Munda People these people migrated from East Asia and shared genetic similarity with people of Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, Japan and China. Unlike the previous two migrations waves, these new migrants were predominately male. Austro Asiatic people spread from Eastern India to Afghanistan and mingled with early hunter gatherers.
In Himachal Pradesh Munda language substrate is found everywhere. These people after mingling with early hunter gatherers truly dominated the Himalaya. In fact majority of Places name of Himachal Pradesh has Austric origin. You can find them in every part of Himachal. They introduced many important cultural elements in present day Himachal. That we will discuss in another post.
Steppe Pastrolist ( 2000 BCE and 1500 BCE )
Aryan People enter India from North-West after crossing Hindu-Kush mountain roughly around 2000 BC. Aryan were pastoralist people heavily dependent upon continuous migration. Aryan migration like Austro Asiatic migration was also predominately male specific . Aryan freely mingled with the local population for centuries before strict caste rule was laid down.
In Himachal Pradesh Arayn people called themselves “Khass”, in present days only Brahmin and Thakur identify themselves as Khaas People. Like other migrants they freely intermingled with the local population for centuries until strict caste rules were laid down. Khaas people introduced the Indo-European language to the hills.
Tibbeto Burman ( Around 2000 BCE – 1000 BCE ).
Tibeto Burman people entered India and migrated from the Tibetan Plateau and the Upper Yellow River valley in China, moving south across the Himalayas into Himachal (Kinnaur, Lahaul-Spiti) and Northeast India. In the medieval period they reached up to Chamba and Kangra.
Conclusion
In conclusion we can say early Hunter gather people laid the genetic foundation. Over the centuries different migrant came and bring important change not only in genetics but culture also. Today no single man can claim caste purity, in fact in genetics there is no such thing as pure and impure. Genetics history tell social evolution is complex process which is independent of genetic admixturing and history.