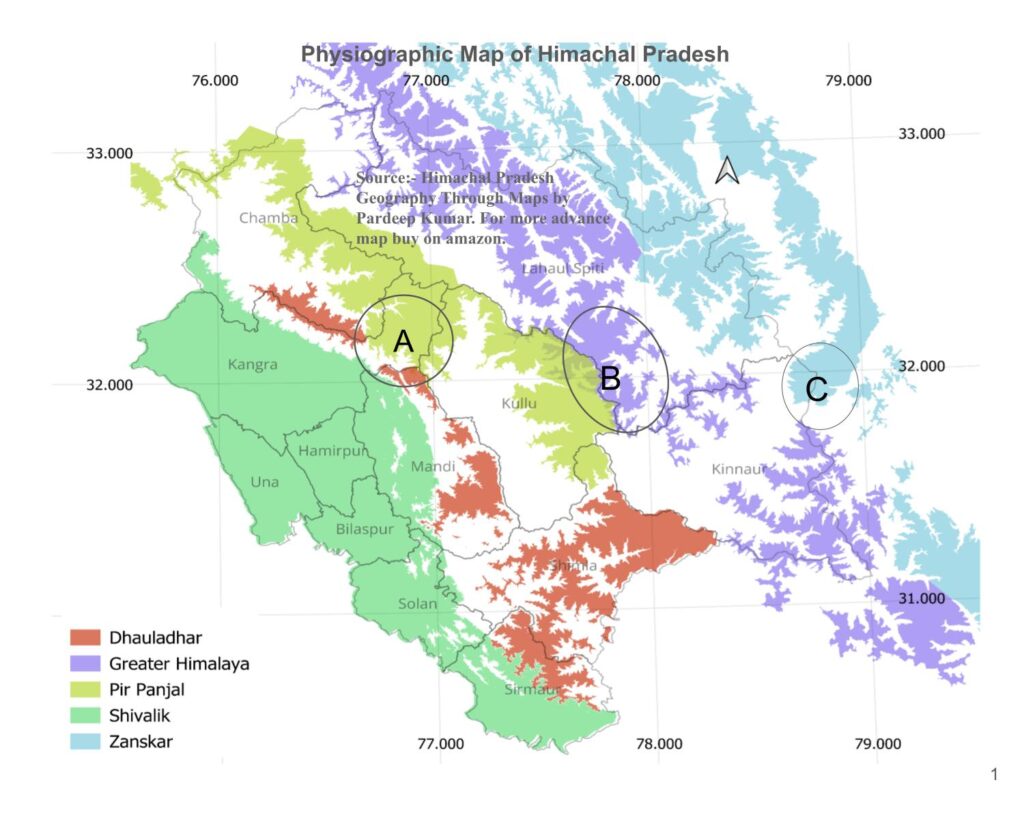
A physiographic division of Himachal Pradesh means breaking the land of area into different regions based on physical features like mountains, valleys, slopes, rocks, altitude, and natural formations. Physiographic Division is different from Geological division.Broadly From west to East Himachal Pradesh can be Divided into 5 Broader Division:
Plain, Shivalik, Lesser Himalaya, Higher Himalaya/Greater Himalaya,Trans Himalaya/Zanskar.
A) Plains of Himachal Pradesh
Plains: Although Himachal Pradesh lack true Indo Gangetic types De-positional Alluvial Plains. But the valleys and foothills of Shivalik hold significant area under Plains. In fact Plains are most important Physiographic division within Shivalik. Confined only to Kangra, Una, Sirmaur and part of Mandi, these plains are densely populated and fertile region of state. Plains area of Himachal Pradesh can be classified into following;
Kiar Dun Plains: These are the southernmost De-positional and Piedmont Plains of Himachal Pradesh. River Bata cut these plains into two equal parts. While river Giri transverse through eastern part. Total Area of these plain is approximately 166 km sq and human density is approximately 950 person per kilometer square.( Census 2011).Demography of Himachal Pradesh, Census 2011 with Maps.
Solan Plains: These are also Piedmont type plains, total area of these plains is approximately 338 km.sq. The region is highly industrialized and probably Pharmacy of world. Total human density is 650 person per Sq.km.
Una Plains: Drained by river Swan river, these are largest plain of Himachal Pradesh. In Monsoon season river Swan deposit fresh Alluvial soil to these Plains. Total area of these plain is 618 km sq and human density is 580 person per sq.km.These plains are intensively exploited for agriculture however Industrial activities are less intensive than Kiar dun and Solan. However in recent time it has become important Industrial hub.
Indora Plains: Total area of these plains 379 km.sq. River Beas bisect these plains in two parts. Indora Plains are good example of Piedmont plains. In recent time this zone has also become important hub of Industrial Activities.
Below is 3D Map of Physiographic division of Himachal Pradesh .
( In above Physigraphic map of Himachal Pradesh:- Greenish Blue-Shivalik, Yellow -Dhauladhar,Red-Pripanjal, Green-Greater Himalaya and Blue -Zanskar)
B) Shivalik of Himachal Pradesh
Shivalik is region of low altitude hills, occupying area between Indo Gangetic Plains and lesser Himalayas It is a vast geographical terrain roughly constitute 25.50% of total State area. Width of Shivalik vary across its span for example in central Parts of state it is roughly 80-85 Km and it southern part in district Sirmour it is just 15-20 Km. Districts likes Una , Hamirpur and Bilaspur are entirely located in Shivalik hills.This is most important Physiographic Division of Himachal Pradesh.
The elevation of the Shivalik varies markedly across its expanse. While the northern and southern regions have higher elevations, the central region is characterized by comparably low heights. For instance, the average elevation of prominent peaks such as Hathi Dhar stands at 1500 meters, Jawalaji Dhar at 1000 meters, Chintpurni Dhar at 800 meters, Bandala hills and Sikandar Dhar at 2000 meters.
This zone encompass Low hills, Piedmont plains and few man made water Tanks. Shivalik spread over the large the part of state in district :- Chamba, Kangra, Hamirpur, Una, Bilaspur, Solan ,Mandi and Sirmaur.Shivalik hills are also famous for their wide Doon valley such as Una Doon, Solan Doon and Pong Valley etc. Two large man made Dam of Himachal have also been constructed in these Doon. 60-65% of Himachal’s population live in Shivalik zone. The Kangra Agricultural System a GIAHS Perspective on Heritage and Resilience.
C) Lesser Himalaya
Lesser Himalaya: Altitude of Lesser Himalaya ranged from 2000 mtr to 4500 mtr. Lesser Himalaya cover approximately 32-35% of state area(Dhauladhar and Pirpanjal). Higher reaches of Lesser Himalaya remain permanently covered under the snow for most part of the year and has Temperate and Alpine types climate, while the lower part received significant snowfall in winter season and has Sub Tropical and Temperate types climate.Climate Classification of Himachal Pradesh.
Lakes, Meadow, Deep Valleys, Passes and Glaciers dominant the overall landforms of this region.Lesser Himalaya further be divided into Dhauladhar and Pir Panjal. Dhauladhar has comparatively lower altitude than Pir Panjal. It start rising at the bank of Ravi and transverse through Chamba, Kangra, Kullu, Mandi ,Shimla , Sirmaur and finally merge with Greater Himalaya after being bisected by Satluj at Rampur. Dhauladhar is further bisected by Beas at Larji in Kullu district and by Ravi in Chamba district.
Ravi valley & Chamba are located between Dhauladhar and Pir Panjal, Kangra valley is located on southern slope of Dhauladhar, scenic Barot valley is also located on inner ridges of Dhauladhar, where as Karsog, Narkanada, Shimla and Churdhar are important tourist places of this range.
Lesser Himalaya is also place of origin of many important rivers and streams such as Ravi, Beas and Tons etc. It is also home of many important lakes such as Khajjiar, Prashar, Lamdal, Servalsar and Tannu Jubbal Map of Important Lakes of Himachal Pradesh..
Pir Panjal after covering a long distance in Kashmir, enter the Himachal in Pangi Tehsil. It formed the natural boundary between Chamba and Lahaul. Famous Chandrabhaga valley is located between Pir Panjal and Greater Himalaya. Pir Panjal also delineate Chandrabhaga basin from Ravi Basin.
Both Pir Panjal and Greater Himalaya merge near Shrikhand in Kullu District. Pir Panjal is relatively less populated mountain region than Dhauladhar. Pangi, Bharmour and Barabhangal are few important settlement of the region. Pir panjal and Dhauladhar both meet at Bara Bhangal in district Kangra, a southern flank of Pir panjal under the name of Dakini Dhar meet Dhauladhar in Chamba.
Lesser Himalaya also known for growth of many medicinal plants such as Rhododendron, Lingar and Gucchi etc. From the horticulture point of view this region is very important, most apple production of state come from this zone. In fact horticulture is the single most important driving force changing the regional landscape. Increasing trend of replacing dense deodar forest with apple Orchard is very much visible at many places such as Kullu, Mandi, Shimla and Sirmaur. Gaddi and Bakarwal tribes inhabitate this region.
D) Greater Himalaya
Greater Higher Himalaya: Altitude of this range is above 4500 mtr. Most parts of this region remain covered under snow for the most part of the years. Greater Himalaya range passes through Chamba, Lahaul Spiti, Kullu and Kinnaur. It attain peak height at point where it merge with Pir Panjal and Zanskar.Area north of Greater Himalaya is rain shadow zone and receive precipitation only in form of snowfall , thus desert like condition prevail most part of it. However in Satluj valley monsoon penetrate deep into the valley up to the Kalpa. Greater Himalaya is source of many important rivers such Chandra, Bhaga, Spiti and Sangla etc.Population in this part of state is very scanty .
E) Zanskar Range
This range touch the Spiti and Kinnaur and formed the Indo Tibet border. Highest peak of Himachal Pradesh is located here. Higher Himalaya is also mingling point of Indian and Tibetan culture. Spiti and Kinnaur are important settlement of higher Himalaya.
Source Book – Himachal Pradesh Geography Through Maps by Pardeep Kumar and Geography of Himachal Pradesh by Pardeep Kumar.(Books are available on Kindle, Amazona and selective retail shops).
Note: Area and population data presented here have been calculated using QGIS 3.40.5, based on vector layers from the Survey of India and Census datasets, projected in CRS EPSG:32643 (WGS 84 / UTM zone 43N) for Himachal Pradesh. Minor variations may exist due to dataset precision and projection methodology.