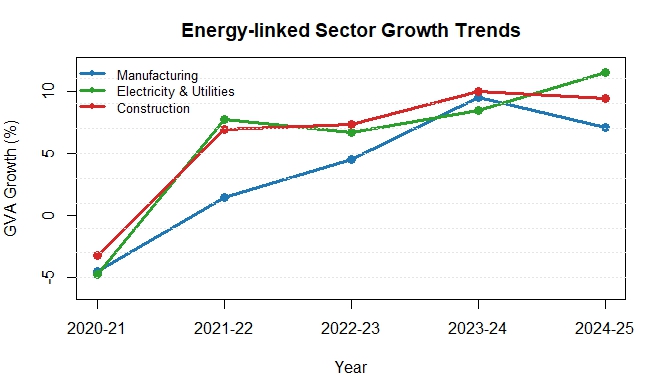
Himachal Pradesh has immense energy Generation Potential. Directorate of Energy is nodal Department controlling the energy sector in Himachal Pradesh. Electricity form the major form of energy. Economically Electricity sector is the part of Secondary sector and is fastest growing sector within that Category. In 2024-25 its growth is expected to be 11.5 %. Electricity is one of the factor that invite manufacturing sector investment.
Player in Energy Sector.
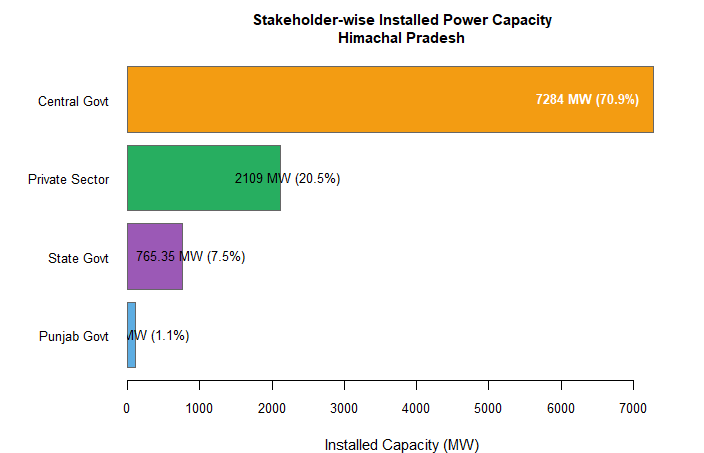
Energy Sector/Electricity Sector of Himachal is dominated by Central Govt Enterprises, State Government Enterprises and Private Sector.
Role of State Govt : HPSEBL, HPPCL, HPPTCL and Him Urja are the Key players of electricity sector. Total Installed capacity of HPSEBL is 489.35 MW , HPPCL’s 276 MW , HPPTCL deal with power transmission and Him Urja look after electricity Projects Upto 5 MW.
Punjab Govt: Punjab Govt has total installed capacity of 110 MW in Shanan Project . State Govt is in talk of taking back the ownership of project from Punjab Govt.
Central Govt: Central Govt has total 7284 MW installed capacity in State. SJVN Limited, BBMB, NHPC and NTPC are major central govt enterprises having operation in state.
Private Sector: Private sector play key sole in generation of hydroelectricity, it has total 2109 MW installed capacity.
River wise Hydro Electricity Sector
Which has vast network of river here is riverwise hydro electricity potential,
| River Basin | Estimated Potential (MW) | Relative Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Sutlej | ~13,332 | highest, backbone basin |
| Beas | ~5,995 | second most important |
| Chenab | ~4,032 | high but under-developed |
| Ravi | ~3,237 | moderate, distributed hydro |
| Yamuna (Tons–Giri) | significant (not precisely quantified) | strategic & multipurpose |
Challenges of Hydro Electricity Sector
1.) Environmental Challenges :Hydropower projects in Himachal Pradesh are located in fragile Himalayan ecosystems. Construction of dams, tunnels, and roads leads to deforestation, slope instability, and disturbance of river ecology.
Frequent issues include:
• landslides and slope failures
• alteration of river flow and sediment transport
• loss of aquatic biodiversity
Climate change has intensified these problems. Erratic rainfall, cloudbursts, glacier retreat, and changing snowmelt patterns have increased project risk, cost overruns, and operational uncertainty. Snowless winter is becoming new problem for hydro Project. ( See more information here )
2.) Geological Challenges: The Himalayan region is geologically young and unstable. Many hydroelectric projects face unexpected geological surprises during tunnelling and dam construction.
Common problems are:
• weak rock strata
• high water ingress in tunnels
• fault zones and shear zones
These issues cause delays, cost escalation, and in some cases, redesign of projects. Projects such as large storage and run-of-river schemes have been particularly affected. Contruction of Hydro Projects are also being opposed my using blasting methods.
3.) Hydropower development often involves land acquisition and displacement of local communities.
Key concerns include:
• rehabilitation and resettlement disputes
• local opposition due to perceived loss of livelihoods
• concerns over safety of dams and tunnels
Public resistance has increased in recent years, especially in river valleys where multiple projects are clustered.
4.) Although generation capacity has increased, power evacuation infrastructure has not always kept pace.
Challenges include:
• difficult terrain for transmission lines
• forest clearance for transmission corridors
• delays in commissioning substations
Even with the efforts of HPPTCL, evacuation bottlenecks can delay the full utilization of commissioned projects. Given the shortage of Land , it is difficult to acquire land.
5.) Hydropower projects are capital-intensive and have long gestation periods.
Key financial challenges:
• rising construction costs
• interest burden due to delays
• reduced financial viability for private developers
Smaller developers, especially in the small hydro sector, face difficulty in sustaining projects under these conditions.
6.) Despite recent progress in solar and alternative energy, the state remains heavily dependent on hydropower.
Any disruption due to:
• climate events
• technical failures
• legal or environmental restrictions
can significantly affect power availability and revenue.
7.) Projects involving inter-state rivers and shared ownership (such as older legacy projects) face:
• ownership disputes
• power-sharing issues
• political negotiations
These complexities slow decision-making and affect long-term planning.
FAQ
Q) How Much Hydro Installation Central Govt Posses in Himachal Pradesh ?
Ans :7284 MW (Approximately)
Q ) How much Electricity Sector Grew in 2024-25 ?
Ans: 11.5 % Growth Rate.
Q ) How much Share does Private Sector has in total installed capacity ?
Ans ; 20.5 % Share in Total capacity.