Introduction
Himachal is prone to very diverse disaster Profile.Total Area of Himachal Pradesh is about 55673 sq Km with Population around 70 Lakh. The overall density as census 2011 was 123 person per square Km, which now must be around 125 person per Sq Km. Physiography of State range from Plain to Higher Himalaya to Cold Desert, which pose wide diversity of threat. ( Details of Whole Disaster Plan can be sen here https://hpsdma.nic.in/)
Factors Affecting the Disaster Profile of Himachal Pradesh.
- Geology: It include Major Thrust , fault, Rocks strata, Slopes etc.
- Climate: It include intense rainfall, Snowfall , Flood and Drought.
- Vegetation:- Like Forest, which is liked with slide and forest fire.
- Industrial:- Like Factory fire, Gas Leaks, Blasts in factory premises.
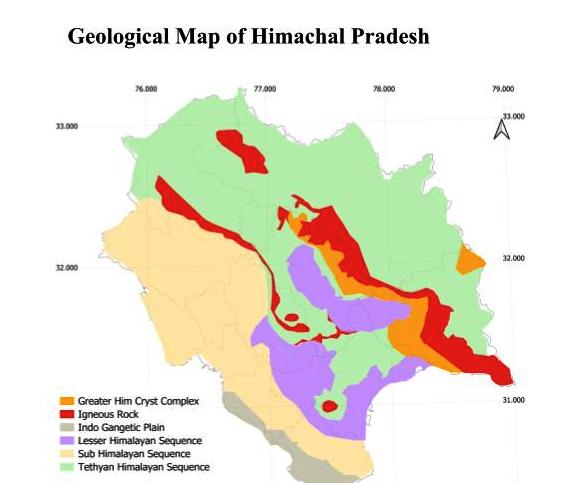
1) Geology of Himachal Pradesh and Disaster:
Himalaya are the youngest Mountain range of world, with many active Thrust and Fault. ( See full Geology of Himachal Pradesh Basic Geology of Himachal Pradesh .)
- Main Frontal Thurst– It separate the Indian Shivalik from the Indian Plains.
- Main Boundary Thrust: This Thrust separate the Shivalik range form Lesser Himalaya.
- Main Central Thrust; This thrust separate the lesser Himalaya and Greater Himalaya. Its passes close to Main Boundary thrust and passes through center of Himachal Pradesh.
Above mention Thrust are major one, there are many local Thrust and Fault such as Kaurik–Chango Fault, Kangra Fault Zone etc , which can case intense earthquakes and landsliding. Specially the area which is near Main Boundary Thrust and Main Central Thrust are very prone to Disaster.
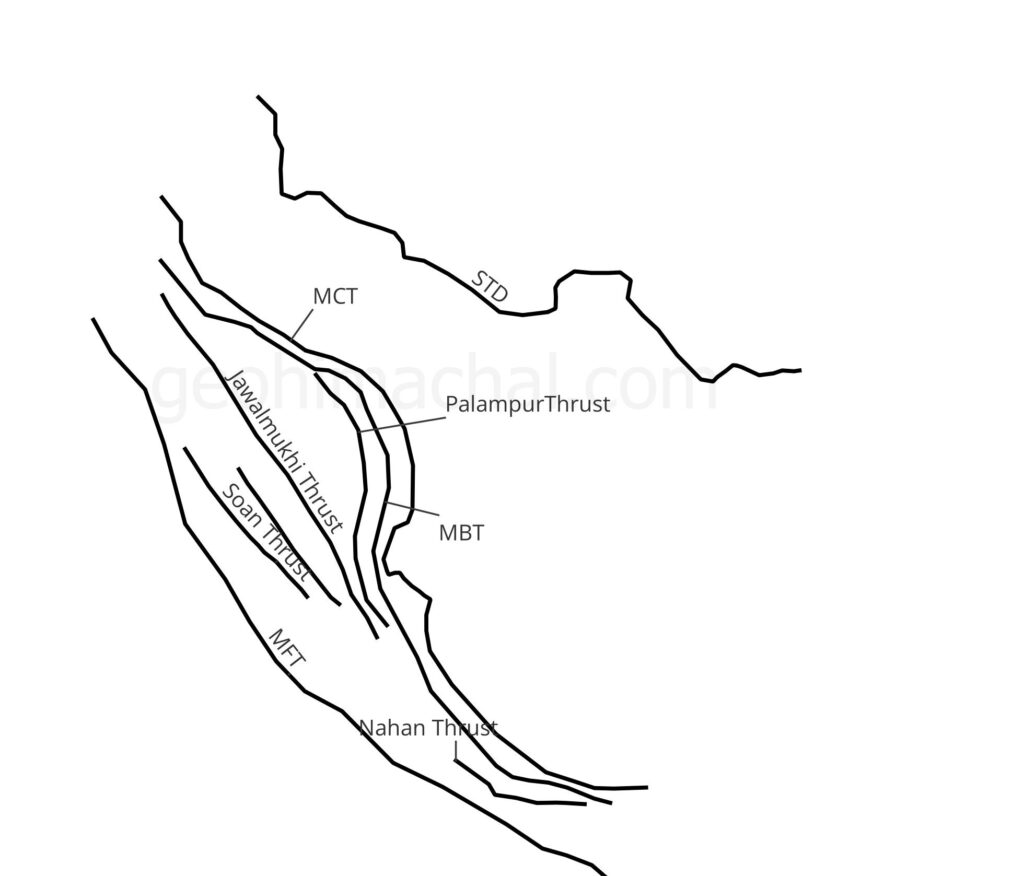
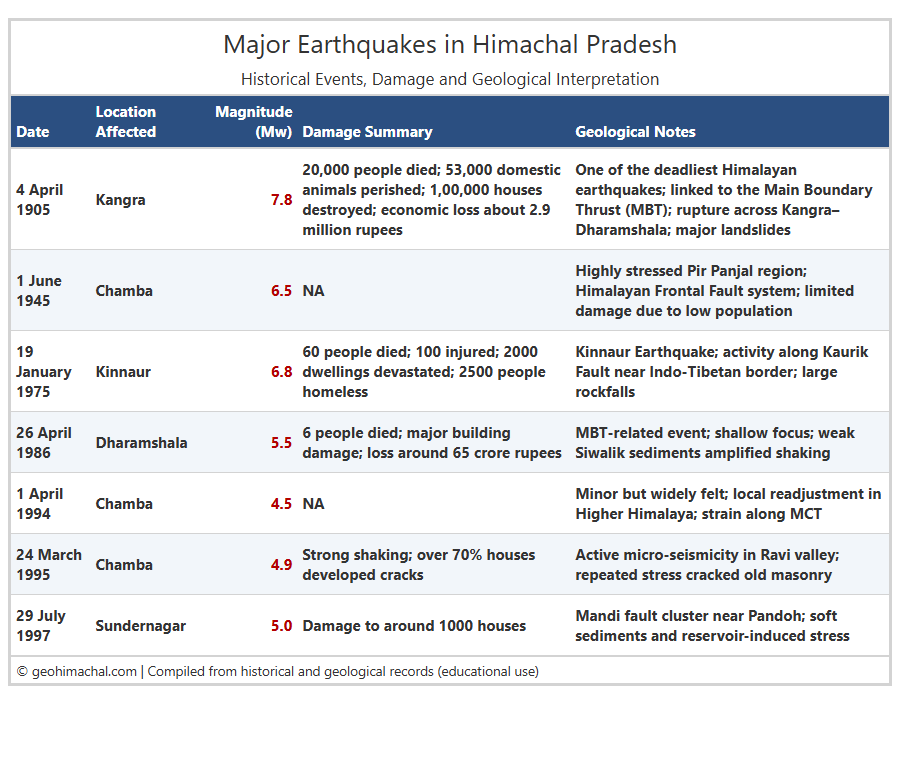
Table of Major Earthquake of Himachal Pradesh
Table Showing Major Earthquake , Magnitude, Damage Summary and Geological Note.
Real Life Example of Thrust Linked Sliding Zones in Himachal Pradesh:-
There many active Sliding zone near Chowari Chamba, along the Dhauladhar and Hathi Dhar.(See the Pic). Similarly there are many active sliding zone in Himachal Pradesh, Marking them and extensive geological studies and associated construction guideline can mitigate disaster risk.
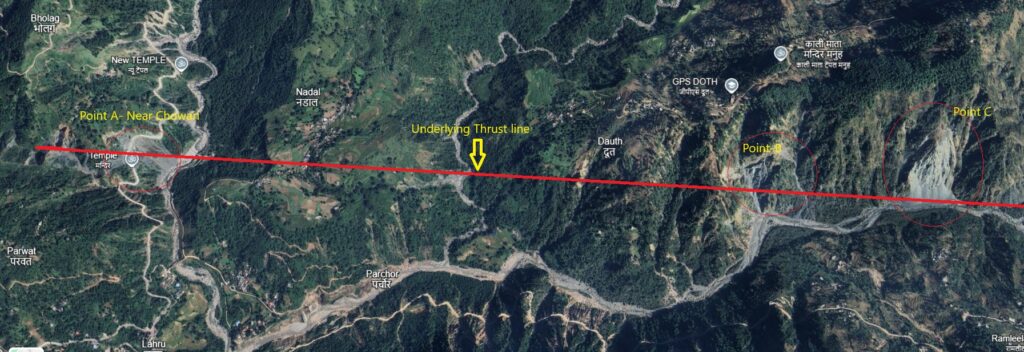
H.P Source- Google Earth Pro.
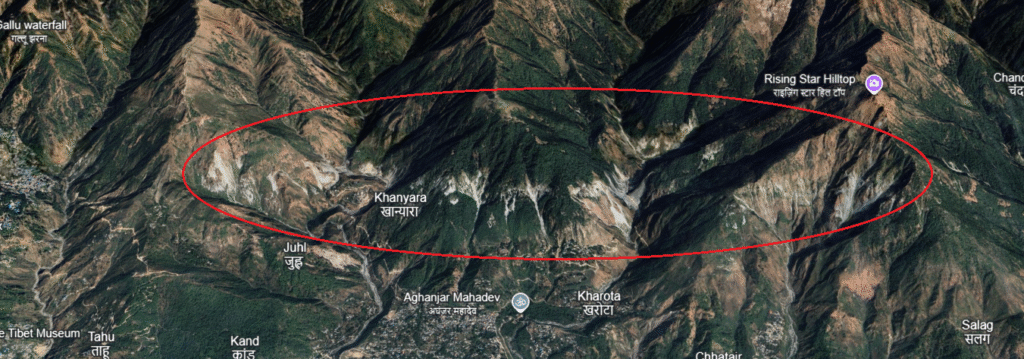
1.1) Rocks of Himachal Pradesh
Rocks of Himachal range from early Quaternary to Pre Cambrian age. Igneous rocks and meta sedimentary rocks are stable than Sedimentary rocks. However underlying thrust and Fault define the stability of a region. Below is simple classification of rocks. (see full Geology here:Simplified Geological Map)
- Higher Himalaya: Oldest crystalline rocks (Precambrian gneiss, schist) + Paleozoic sediments.
- Tethys Himalaya (Spiti–Kinnaur belt): Marine sedimentary rocks from Paleozoic to Mesozoic (limestone, shale, sandstone).
- Lesser Himalaya: Meta sediments (slates, phyllite, quartzlite) and Subathu Formation.
- Shivalik Foothills: Youngest fluvial deposits (Miocene–Pliocene conglomerates, sandstones).
- Valley Fills: Quaternary alluvium, moraines, loess.
Rocks Link with Disaster
Rocks which are sedimentary in nature are very unstable and can cause major landslide events. In contrast igneous rocks and meta sedimentary rocks are relatively stable and are less porus. For example Shivalik is composed of sedimentary rocks like sandstone, madstone and silt stone etc thus it cause sheet erosion.
Real Life Example:
In 2017 , mud flow in Shivalik hills in District Mandi caused massive landslide and killed 46 People. If rocks Data is studied with underlying thrust , this kind of disaster can easily be aborted.

1.2) Slope and Disaster Profile of Himachal Pradesh.
Slope region define the intensity of landslide. Underlying Thrust/Faults, Forest cover, Rocks and Rainfall are major factors defining the intensity of Landslide. Thus we can say:
Landslide= F (Thrust, Forest, Rocks and Rainfall)
Where are Slope are unstable:
Slope are Generally unstable where Thrust are active. In case of Himachal Pradesh, you will be find Lesser Himalaya and Greater Himalaya has very unstable Slope due to on going collision of Himalaya.
Unstable Slope=F( Thrust, Rocks, Rivers and Infrastructure Like Highways)
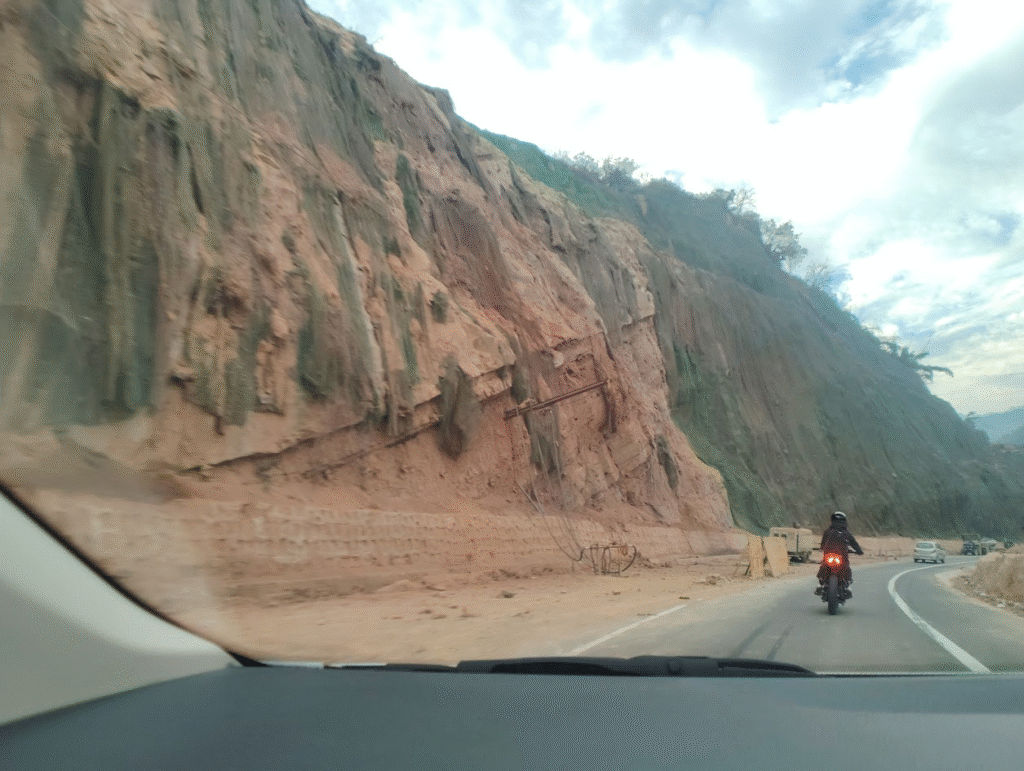
Real life Example
Four Lanes construction has destabilized the slope along the Chandigarh Shimla highways causing serious threat to commuter. Similarly Shimla and Matour highway has opened new sliding zone specially near Ranitall and Kangra.

2. Climate Related Disaster
In included heavy rainfall, snowfall, cold and hot winds ,Drought and GLOF events. In recent years monsoon days has been decreased with intensity of monsoon has significantly increased, similarly mountain are experience Dry , snowless winter spell all this impacting the fragile Ecological system. Climate change has also increased the intensity of GLOF events in Himacha Pradesh.
Latest Modeling and Use of AI in GLOF events
Researcher has will automated system to detect glacial lakes in Himachal Pradesh using satellite images and machine learning. It combines data from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, SRTM DEM and high-resolution Planet Scope images. A Random Forest model identifies glacial lakes with high accuracy (up to 94.44%).
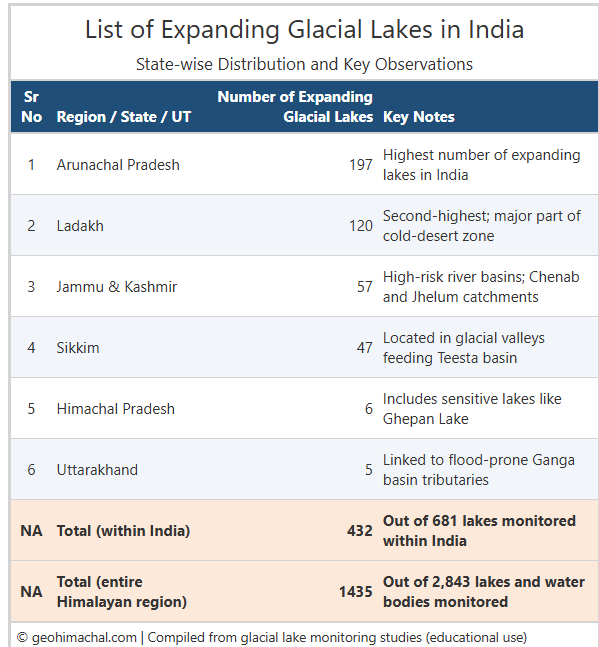
Source – Indian Express-June 2025.
3.Vegetation
Forest cover 27.99 % area of Himachal Pradesh. Plant roots bind soil, making slopes more stable and lowering the chances of landslides in hilly regions. Forests act as natural barriers by slowing runoff, reducing floods and improving water infiltration.

Thick vegetation also protects riverbanks from erosion and prevents the widening of rivers during heavy rain. In dry areas, vegetation shields the land from wind erosion and dust storms. When forests are cut or degraded, these protective functions disappear, turning small hazards into big disasters. Healthy vegetation, therefore, acts like a natural defense system that protects both people and landscapes.
Real life Example:
Channelization and afforestation under the JICA project has reduce the flood potential in Swan river catchment area in district UNA. Similarly people of Kullu protesting the cutting of tress for Bijli Mahdev project, highlight the role vegetation in Disaster. Similarly pine leaf needle in hot summer make many region fire prone.
4. Industrial Factors
Like Factory Fires, Current , Blast, release of chemicals etc. pose serious threat in industrialist and urban zone. District Una, Solan, Sirmaur and part of Kangra are prone to this kind of disaster. Infamous Industrial Disaster included Haroli’s fire cracker factory blast. As Industrialisation of Himachal Pradesh is increasing industrial threat are also increasing.
Other Potential Threats :- A large Gas Plant of HPPCL in Una, Chemicals Factories of Nahan and Baddi and Steel Plants are very prone and need strict regulation. Govt need to assist in Technology up gradation and ZED certification. Steel Plant in Himachal are work on very old technology and manual assembly line.
5. House Fire
House fire are commonly in almost in all seasons in Upper Himachal Pradesh, where house are build with locally available wood. House fire generally began with kitchen fire, electric circuit and other human induced factors. Poor section of society is generally prone to House fire.Such a disaster can be prevent with distribution of Fire Detector from Govt Depot.
6. Road Accident
Deep valleys and Fragile road with very low visibility make Himachal Pradesh are very Prone to road accident. Road become more disaster prone in winter when water or moisture fridge on road making it slippery. Road widening, speed meter and strict implementation of law can reduce road related disaster.
7. Snow Less winter
Snowless winter make rocks and Soil very dry. It further limit the vegetation growth. When rain come it rocks easily disintegrate and soil erode.( See further )
Solution
- Mapping of Major and minor Thrust zone and restricting the construction near active zone.
- Installation of Small sonar through out the state to improve forecasting.
- For Flood Prone area, a law available but implementation is very poor.
- Distribution of Fire Detector through Govt Depot especially in Selected Fire Prone Panchayat.
- Developing an app to report and share Potential Threat type or zone in state.
- Use of Drone and satellite to fire detection and fighting.
- Setting Volunteer Committee at Local Level.
- Assigning Disaster related role to different Departments to further decentralization of Decision making.